Web 3.0, AI, and the Future of the Internet
Introduction
ChatGPT was introduced by OpenAI in November 2022. It is a generative AI model, first announced by CEO Sam Altman. OpenAI was a non-profit organization before 2015, but became a for-profit entity after 2019.
Journey Of OpenAI
AI was first introduced in 1956 during the Dartmouth workshops. It gained momentum between 1980-1987 when various companies and governments, particularly the Japanese government with its Fifth Generation Computer Project, began funding AI development.
Public interest surged before the introduction of ChatGPT, especially following the news of Elon Musk’s AI defeating a champion gamer in 2017. In 2019, the ESA Dextrous Robot Arm (DexArm) project attracted attention by demonstrating its ability to learn human behavior, utilizing OpenAI technology. The launch of DALL-E in 2020 marked another significant milestone, evolving from a concept OpenAI first discussed in June 2020, originally called Image GPT.
About CEO of OpenAI
Sam Altman was born in Chicago on April 22, 1985. He exhibited a keen interest in technology from a young age, receiving his first Macintosh SE computer at age 8. His early experiences included exploring AOL chat rooms. Altman studied Computer Science at Stanford University, but dropped out in 2005 to co-develop a mobile app called Loopt, which shared users' live locations with friends, similar to Facebook. The app was funded by Y-Combinator and Sequoia and has been instrumental in navigation since its inception in 2004, offering real-time updates and user-friendly interfaces.
Sam Altman's Experience
Understanding ChatGPT:
ChatGPT is an advanced conversational AI program that mimics human-like interactions. Users can type prompts, and it responds as if in a natural conversation. It serves various purposes, from virtual companionship to educational assistance. ChatGPT is a generative AI model built with Python and primarily functions as a narrow AI, performing specific tasks.
It employs several machine learning algorithms, including reinforcement learning, where correct actions receive rewards and incorrect ones incur penalties.
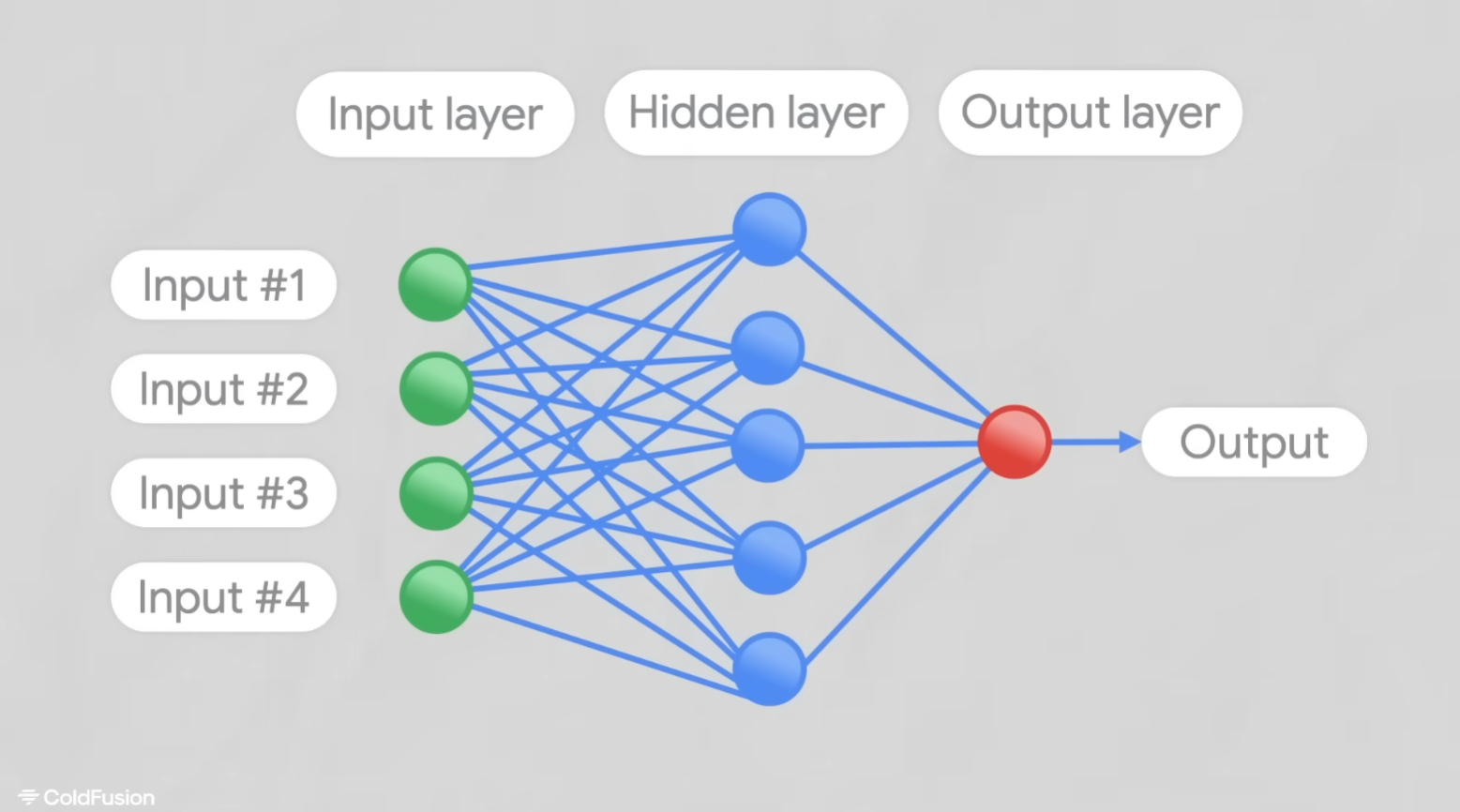
 Infrastructure of these algorithms
Infrastructure of these algorithms
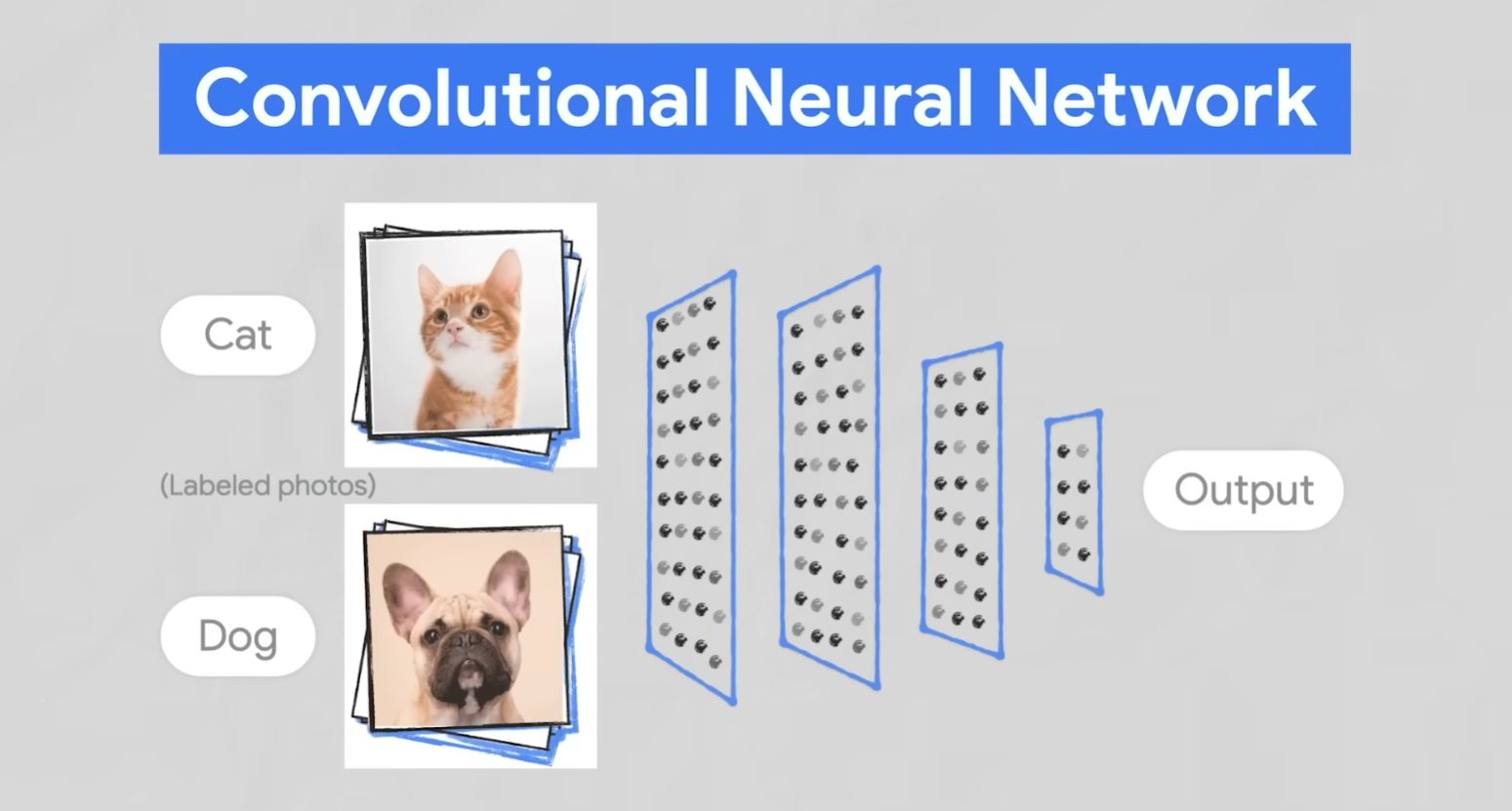
Key Algorithms in ChatGPT:
- Convolutional Neural Networks
- Transformer Models
- In-depth Convolutional Neural Networks
ChatGPT excels in generating content across various formats, including text, images, and audio, and is heavily reliant on Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Generative AI
Generative AI combines several AI models, including:
- Discriminative AI: Used for classifying objects based on datasets.
- Reactive Machines: Algorithms used in self-driving cars.
- Theory of Mind: Employed in chatbots for general conversation.
- Narrow AI: Executes singular tasks, such as in e-commerce.
- Supervised Learning: Involves training on labeled data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Identifies patterns without labeled data.
- Reinforcement Learning: Rewards or penalizes based on model performance.
Web 3.0 vs Web 2.0
- Decentralized Experience: Web 3.0 focuses on decentralization and blockchain technology, giving users greater control over their data and improving privacy.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Web 3.0 is designed to integrate smoothly with mobile devices and various data sources, unlike Web 2.0, which did not fully utilize IoT potential.
- Data Storing Web-Experience: Web 3.0 processes and stores data for optimal output, unlike the centralized data management of Web 2.0.
- AR, VR, and Intelligent Automation: Web 3.0 emphasizes immersive experiences using VR and AR technologies.
Apps Comparison
| Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
|---|---|
| Presearch | |
| Status | |
| Spotify | Audius |
| YouTube | Odysee |
| GitHub | Hugging Face |
| BrainTrust |
More on ML Models
- Variational Autoencoders (VAE): Used for anomaly detection, particularly in financial fraud and manufacturing defects.
- GitHub Copilot: Assists in writing code in GitHub repositories, based on OpenAI's Codex model.
- Microsoft Bing Chat: A direct part of ChatGPT that allows for more customized responses.
- Text-To-Image Models: Such as DALL-E and Midjourney, which help reduce human effort in image generation.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Comprising a generator and a discriminator, these models create content while ensuring high quality through a multistep process.
Future of AI
- Enhancing computer graphics and animation, especially in gaming and film.
- Predicting renewable resource demands and managing distribution networks.
- Simulating designs for large-scale projects.
- Innovating materials in the textile industry.
- Generating audio assets.
Dangers of AI
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, warned, “Using AI is like summoning the demon; AI is far more dangerous than nukes,” highlighting the potential risks of AI.
Conclusion
Instead of fearing AI's potential to replace jobs, we should explore how we can leverage it to enhance our daily activities.
© 2024, Built with love by heramb.